Painful bladder and backache are common complaints for some women. Those who are experiencing health issues in the pelvic region can seek help from an obstetrician-gynecologist (OB-GYN), but going to a urologist could be a better option. Thus, the following questions arise: Can a gynecologist treat urinary tract infections (UTIs)? Can a gynecologist treat a woman’s aching bladder?
Although women’s urologic and reproductive systems are close together in the body, both systems, regardless of their proximity, require different expertise and specialties to pinpoint the right diagnosis and proper treatment. Of course, there are different specialties for different ailments.
A urologist specializes in the urinary system, which comprises the urinary bladder, ureter, and urethra. A misconception exists that urologists only treat men’s healthcare issues, but they treat women’s too. They provide care related to the urinary tract, including overactive bladders and blood in urine, otherwise known as hematuria.
A gynecologist specializes in the female reproductive system. They provide healthcare related to the reproductive organs, including menstrual cycle problems, fertility, and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
The urinary tract and female sex organs have a lot of overlap in the body, so gynecologists and urologists can work collaboratively to address their patients’ needs.
What is a UTI?
A UTI is an infection in part of the urinary system. This system is made up of the kidneys, the ureter, the urethra, and the bladder. Any one of these parts can be infected, but usually, the bladder and urethra are the worst affected. If the infection is left untreated, it could spread to your kidneys, potentially leading to serious diseases. Research shows that UTIs are one of the most frequent bacterial infections that women face, with almost 50%–60% experiencing it in their lifetime. An estimated 20%–30% of women have recurrent UTIs within the space of 6 months or three within a year.
What questions gynecologist might ask?
- Do you have foul-smelling or irregularly colored urine or vaginal discharge?
- Do you feel lightheaded or dizzy?
- Are you drinking enough water?
- Have you ever had kidney stones?
- Have you ever been hospitalized for UTIs?
- Is there any possibility you have an STD?
- Is it possible you are pregnant?
- Do you have any medication allergies?
- Have you ever been treated for a UTI in the past?
What questions do you need to ask your gynecologist?
Do I need to take a urine test?
If a physician suspects a woman has a UTI, a urine sample will be collected for further testing. Remember, when you are giving a urine sample, it is important to do a ‘’clean-catch’’ to ensure good results.
After taking a urine sample, the urine will be tested in the clinic with a urine strip or ‘’dipstick’’, which gives immediate results. The urine may be sent to a lab for more reliable information, but it can take a few days.
Am I at risk of getting UTIs?
The female anatomy makes women more susceptible to UTIs than men. This is because the urethra in a female body is shorter than in a male’s, creating easy access for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Women who are sexually active are more prone to UTIs. Women who are active with more than one partner are at greater risk of exposing themselves to bacteria.
- The decrease in estrogen during menopause could make the body more vulnerable to UTIs.
- The use of a catheter to urinate can increase risk.
- Kidney stones create an obstruction in the urinary tract and contribute to UTIs.
- Autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or decreased immunity may create a lower defense against fighting microorganisms that cause sickness or infections.
What are the symptoms of UTIs?
- A strong urge to urinate that does not go away.
- A burning feeling when urinating.
- Urinating often or passing a small amount of urine.
- Cloudy urine.
- Urine that appears red or brown in color are signs of blood in the urine.
- Strong, foul-smelling urine.
- Pelvic pain in women—especially in the center of the pelvis and the area around the pubic bone.
Types of UTIs
Each type of UTI may result in specific symptoms, but the symptoms depend on which part of the urinary tract is infected.
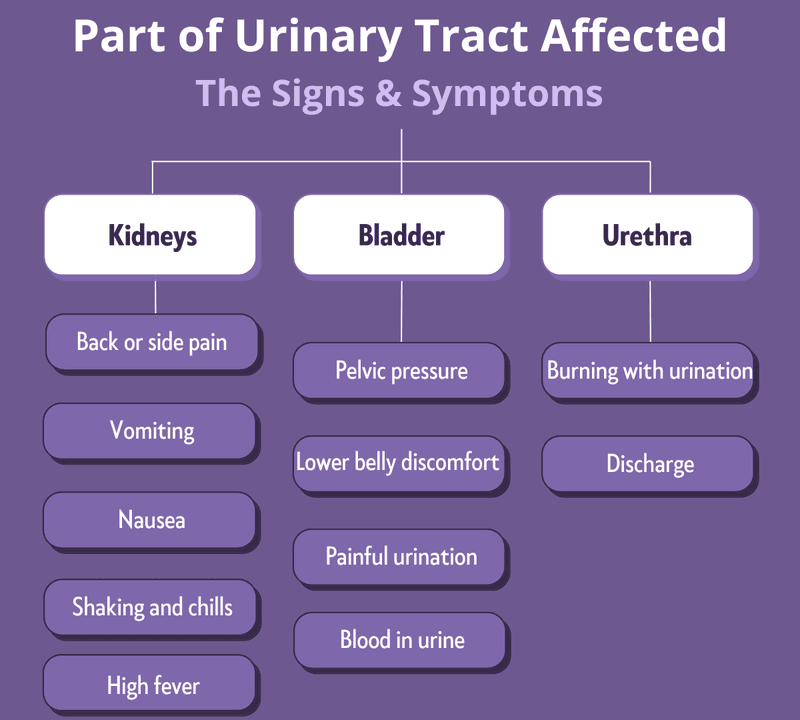
What are the causes of UTIs?
UTIs mostly occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to spread in the bladder. The urinary system is designed to keep bacteria out, but sometimes, the immune system fails. When this situation happens, bacteria may take hold and grow inside the urinary tract.
The most common UTIs occur mainly in women and affect the bladder and urethra.
1-Infection of the bladder:
This type of UTI is caused by Escherichia Coli and is most commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes, having sex may also lead to a bladder infection, but you don’t have to be sexually active to develop one. All women are at risk of bladder infections because of their anatomy. In women, the urethra is close to the anus, and the urethral opening is close to the bladder. This makes it easy for bacteria around the anus to enter the urethra and travel to the bladder.
2-Infection of the anus:
This type of UTI occurs when GI spreads from the anus to the urethra. An infection of the urethra can be caused by STDs, including herpes, gonorrhea, and Mycoplasma. This happens because a woman’s urethra is close to the vagina.
Can a gynecologist be more than a pap-smear doctor?
Treatment for UTIs
Treatment plans are determined by the specific infection, severity, and how it comes.
For women with rare UTIs: An antibiotic is likely to be prescribed. Antibiotics are usually the first line of defense for combating a UTI. Based on the severity and type of bacteria, this will result in specific antibiotics recommended for treatment. Symptoms should start to improve within a few days of taking antibiotics. It is best to complete the course of medication prescribed by your doctor to protect you from infection.
For women who experience more frequent UTIs: The treatment plan may look different to accommodate your current health condition. Your gynecologist may prescribe you a lower dose of antibiotics for a few days or weeks for an uncomplicated UTI. For women in the menopause who experience frequent UTIs, your gynecologist may prescribe vaginal estrogen therapy to help balance your hormones, provide protection against bacteria, and stabilize the frequency of UTIs.
life-threatening
- Increased frequency of getting an infection.
- Damage to the kidneys if the infection spreads further into the urinary tract.
- Premature birth or low birth rate for pregnant women.
- Sepsis. This is a condition caused by an infection. When the body cannot respond to the changes occurring in the body, this can lead to organ damage and become life-threatening.
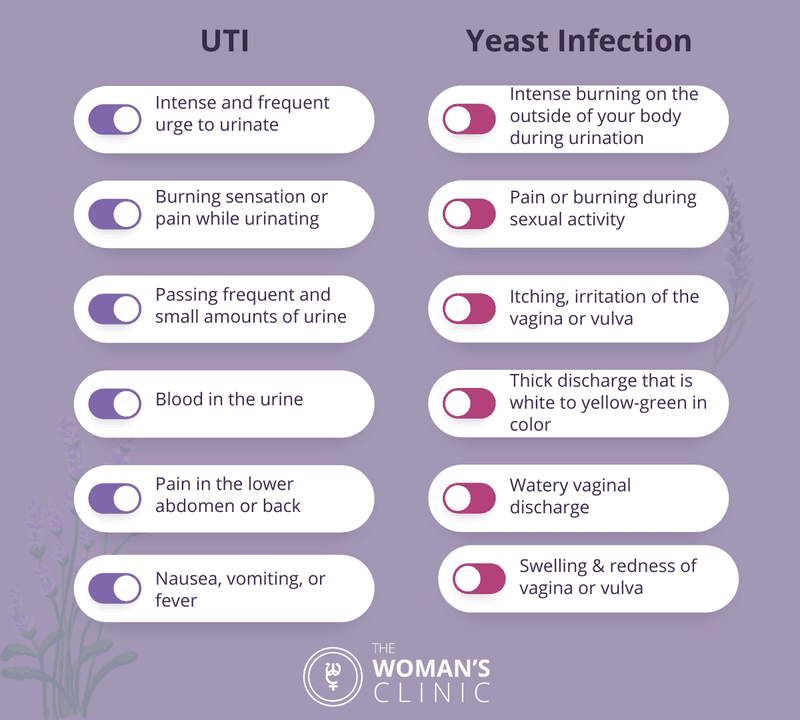
UTI vs. Yeast Infection:
UTIs and yeast infections are different beasts. Typically, UTI infections affect urination, while yeast infection symptoms include pain and itchiness in the vagina and vulva. There is a difference between the two types of infection. When should you call for a doctor?
How to prevent UTIs
1-Drink plenty of water and relieve yourself: The simplest way to prevent a UTI is to flush bacteria out of the bladder and urinary tract before it can settle in. If you are well-hydrated, it will be tough to go too long without going to the bathroom.
2-Wipe from front to back: Bacteria tend to hang around the anus. If you wipe from front to back, especially after a bowel movement, they are less likely to reach the urethra.
3-Steer clear of irritating feminine products: Skip douches, deodorant sprays, scented powders, and other feminine products with fragrances or chemicals.
4-Wear underwear that has a cotton crotch and doesn’t fit too tightly.
5-Urinate after all sexual activity.
6-Take probiotics: Probiotics encourage a healthy immune system, which gives your body the ability to fight off bad bacteria. When you have a UTI, harmful bacteria replace the good bacteria in your vagina, known as Lactobacillus. Probiotics restore the good bacteria that can help you fight off future UTIs.
- Love Wellness Good Girl Vaginal Probiotics
- OLLY Happy Hoo-Ha Capsules, Probiotic for Women
- Garden of Life RAW Probiotics Vaginal Care
- Rae Wellness Vaginal Balance Capsules
- Love Wellness UTI Don’t Think So
- D-Mannose Urinary Tract Health
Think you have a UTI? Call your Gynecologist for UTI treatment!
If you believe you may have a UTI, contact your OB-GYN at The Woman’s Clinic to make an appointment. If you are not currently a patient at The Woman’s Clinic, we are taking new patients and are happy to schedule an appointment for you with any of our experienced and compassionate doctors.

